Keflavik APP
Keflavik Approach (BIKF_APP) provides approach control service to all aircraft within the Keflavik (KF) sector of the Faxi TMA, and area control service to aircraft transiting the KF sector of the TMA. Keflavik APP also bandboxes the RK sector of the TMA when Reykjavik APP is offline.
Arrivals
|
INITIAL FIX |
RUNWAY |
|||
|
01 |
10 |
19 |
28 |
|
|
DEVUD |
4N |
4M |
2K |
1H |
|
NASBU |
4N |
2M |
3K |
1H |
|
ASRUN |
3N |
2M |
2K |
1H |
|
BASLU |
3N |
3M |
2K |
2H |
|
BIRNA |
2N |
3M |
3K |
2H |
|
ELDIS |
3N |
3M |
3K |
3H |
|
GIRUG |
3N |
3M |
2K |
2H |
|
INGAN |
5N |
3M |
2K |
2H |
Reykjavik Control clears aircraft for the STAR & descends them to FL100. If Reykjavik Control is offline, then APP may contact aircraft early (3-5 mins before they reach the first waypoint of the STAR) to issue this STAR clearance and descent.
The standard approach for all runways is the ILS Z approach. BIKF's STARs are designed such that the last waypoint of the STAR is also one of the IAF of the ILS Z approach for that runway.
APP shall descend aircraft such that they reach the last waypoint of the STARIAF at 3000ft whenif RWY 10/19 is in use, or 3500ft whenif RWY 01/28 is in use. The last waypoint of the STAR will also be an IAF for the ILS Z approach.
Traffic permitting, it is common practice during low-moderate traffic for APP to cancel the STAR and routeclear aircraft directly to the last waypoint of the STAR, i.e., the ILS Z approach IAFs.IAF.
To ensure that no aircraft violates the minimum horizontal separation of 3 NM in the TMA, APP shall establish aircraft onto the ILS with no less than 5 NM separation. During single runway operations, APP should aim for at least 7 NM of separation between arrivals, to ensure sufficient gaps for departures.
The ILS Z approaches have a published minimum speed of 160kts until 4 NM from the airport. APP may issue a higher/lower speed requirement, or cancel this speed restriction, as necessary for separation and sequencing.
Arrivals on the ILS Z or RNP approaches may be transferred to TWR as soon as they have passed the IAF. For any other approach, APP should wait until the aircraft is established on final approach track/course.
Non-Standard Approaches
If aircraft are unable to accept the ILS Z approach, then alternative approaches should be offered in order of precision.
RNP & LOC Z
The published RNP & LOC Z approaches largely mirror the ILS Z approaches, and share the same published minimum speed of 160kts until 4 NM from the airport.
Vectored ILS
Aircraft on a vectored ILS approach into BIKF should be established no closer than 10 NM out.
ILS Y / VOR
The ILS Y and VOR approaches at BIKF are non-RNAV ILS procedures. They are teardrop-shaped procedures commencing from KFV VOR. Aircraft requesting these approaches should be cleared direct to KFV as soon as practical. After KFV, aircraft should report beacon outbound, and then established on the ILS/final approach course (as appropriate.)
Due to the added difficulty of sequencing aircraft on these procedures while the ILS Z/RNP approaches are also in use, it is preferred to vector aircraft onto the ILS instead of using these procedures.
Since the ILS Y and VOR approaches requires the aircraft to descend below 3000ft (into the BIKF CTR), APP should coordinate with Keflavik TWR to make them aware of any aircraft on such approaches.
NDB (RWY 10)
The NDB approach for RWY 10 is a racetrack procedure commencing from KF NDB. Aircraft may be cleared direct KF as soon as practical. The aircraft should be asked to report on final approach course, at which point it may be transferred to TWR.
Since the NDB approach requires the aircraft to descend below 3000ft (into the BIKF CTR), APP should coordinate with Keflavik TWR to make them aware of any aircraft on such approaches.
Departures
Traffic permitting, it is common practice for Approach to issue a direct to the last waypoint of the SID immediately after radar identifying the aircraft, even if said waypoints lie outside the TMA This does not require coordination with Reykjavik Control.
LVP Operations
When BIKF is in LVP, Keflavik Approach and Keflavik Tower should coordinate to revise the runway configuration so that the arrival runway is either RWY 10 or 19, as those are the only two CAT II equipped runways at BIKF. Approach should ensure additional spacing (at least +2 NM on top of usual minima) between aircraft.
Final Approach Position (BIKF_F_APP)
The Final Approach position (BIKF_F_APP) is intended to relieve the workload of the primary Approach position during high traffic. The coordination name of BIKF_F_APP is Keflavik Final, and its radio callsign is “Keflavik Approach.”
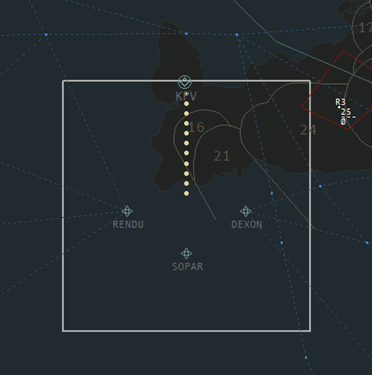
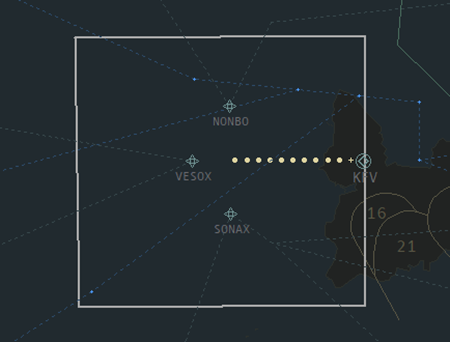
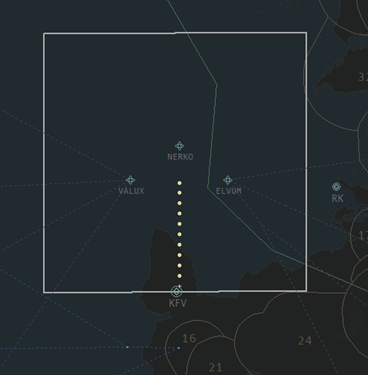
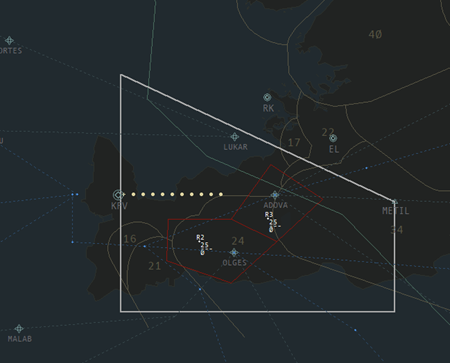
Final controls the airspace immediately surrounding the extended centreline of BIKF’s active arrival runway. Final’s airspace ranges from 3000 – 7000ft. For RWY 01, 10, and 19, Final’s airspace is a large box, roughly 40 NM on each side, around the extended centreline. See the images below for reference.
| RWY 01 | RWY 10 |
 |
 |
| RWY 19 | RWY 28 |
 |
 |
When both Keflavik Approach and Keflavik Final are online, their division of responsibility is as follows:
- Approach establishes the arrival sequence and descends aircraft to 7000ft.
- Approach will hand the aircraft over to Final when the aircraft reaches 7000ft and enters Final’s lateral boundaries.
- If holding is necessary, Approach will initiate and manage the holds.
- Final fine-tunes the sequence and directs aircraft onto final approach (the ILS).
Keflavik Final does not control departures, or control BIKF top-down.
