Reykjavik TWR
Reykjavik Tower (BIRK_TWR) is responsible for BIRK’s runways, and for providing air traffic control service within the Reykjavik Control Zone (BIRK CTR.)
Runway Configuration
Controllers should consider that RWY 01/19 is considerably longer than RWY 13/31 (1567 vs 1230m). Moreover, only RWY 19 has an ILS (RWY 13 only has a localizer, and RWYs 01 and 31 have no precision landing equipment.)
Therefore, aircraft, especially heavier aircraft such as turboprops, jetliners, etc., may prefer or even require RWY 01/19, even if the winds slightly favor RWY 13/31.
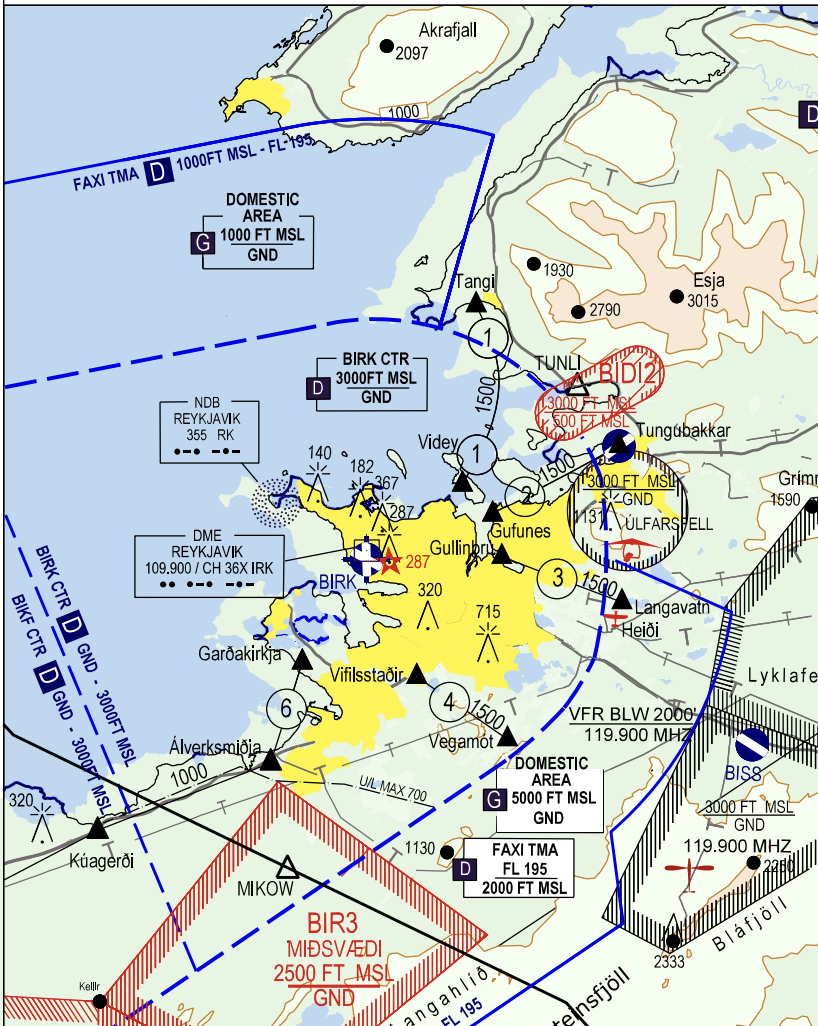
Reykjavik Control Zone (BIRK CTR)
The BIRK CTR ranges from GND – 3000ft. It is directly bordered by the Keflavik Control Zone (BIKF CTR) to the west, and is surrounded by the Faxi TMA above and to the sides.
Traffic Circuit
The standard traffic circuit for BIRK is south of Runway 13/31, and west of Runway 01/19. Therefore, the circuit direction is Left for RWY 01 & 31, and Right for RWY 13 & 19.
VFR Routes
Five VFR routes are published within the CTR for single-engine VFR aircraft – routes 1, 2, 3, 4, and 6 (route 5 is not in use). See the VFR Guide for more information.
VFR departures not on a VFR route should be instructed to report 6 NM out from BIRK. They should be coordinated with either Reykjavik Tower or Keflavik/Reykjavik Approach if they will be entering the BIRK CTR or Faxi TMA, prior to them reaching the relevant airspace boundary.
If an aircraft will not enter the BIRK CTR, and will remain below the Faxi TMA, it may be released to UNICOM without coordination.
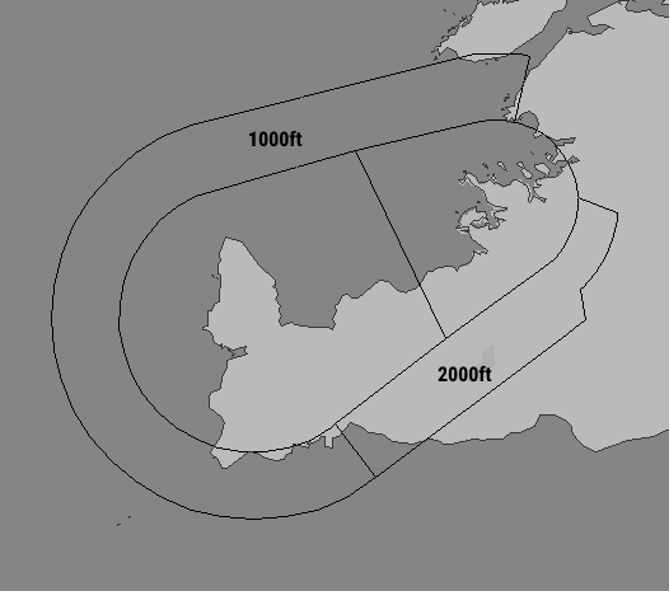
Overlying Airspace: The Faxi TMA
The airspace directly overlying the BIKF CTR is the Faxi TMA (Terminal Manoeuvring Area). Specifically, the Keflavik (KF) sector of the Faxi TMA directly overlies the BIRK CTR. Moreover, the Faxi TMA has “buffer zones” next to the BIRK CTR which extend down to 1000ft and 2000ft respectively. See the image below.
TWR should coordinate VFR aircraft leaving the CTR into the TMA, including the collars, with APP. If a departing aircraft will only briefly enter the buffer zone without entering the TMA itself, and there is no conflicting IFR traffic, APP may simply have TWR release the aircraft to UNICOM.
Special Airspace
Neighboring restricted & training areas include Sandskeid, Sletta, and for the duration of the volcanic eruption on Reykjanes Peninsula, danger area BIR4. When there is activity in these areas, Tower should notify aircraft in the vicinity and add appropriate text to the ATIS, e.g., "GLIDERS OPERATING AT SANDSKEID."
Missed Approach
TWR should instruct aircraft to follow the standard missed approach. If an aircraft is not able to fly the standard missed, TWR should instruct the aircraft to climb straight ahead to 5000ft, or coordinate appropriate vectors with APP.
TWR shall coordinate all missed approaches with APP prior to transferring them to APP.
Clearance Below 2000ft (VFR / Visual App)
Twin- or multi-engine aircraft arriving BIRK which are VFR, or requesting a visual approach, must be cleared below 2000ft by Reykjavik TWR. APP shall coordinate all aircraft with TWR prior to transfer of control; if TWR grants the clearance below 2000ft, then APP may communicate that to the pilot.
In the rare circumstance that traffic congestion in the CTR/circuit do not permit giving clearance below 2000ft as described above, TWR must provide the aircraft alternate instructions (e.g., orbiting/holding away from the airport.) Alternatively, TWR may deny the aircraft permission to enter the CTR.
Next ATS Unit for Departures
Generally, all departures should be transferred to Keflavik APP (BIKF_APP) after departure.
If both Keflavik and Reykjavik APP are online, then TWR should transfer the aircraft to whichever APP sector the aircraft will be entering the airspace of first. If in doubt, confirm with Reykjavik APP.
Reduced Runway Separation Minima
The use of reduced runway separation minima (RRSM) is permitted at BIRK, subject to the conditions outlined in the Tower SOP.
NOTE: Due to the airport layout at BIRK often requiring backtracks, and the shortness of the runways, controllers may find it difficult to obtain the necessary separation distances to apply RRSM.