Sondrestrom APP
Sondrestrom Approach (BGSF_APP) provides an approach control service within the Sondrestrom TMA and CTA.
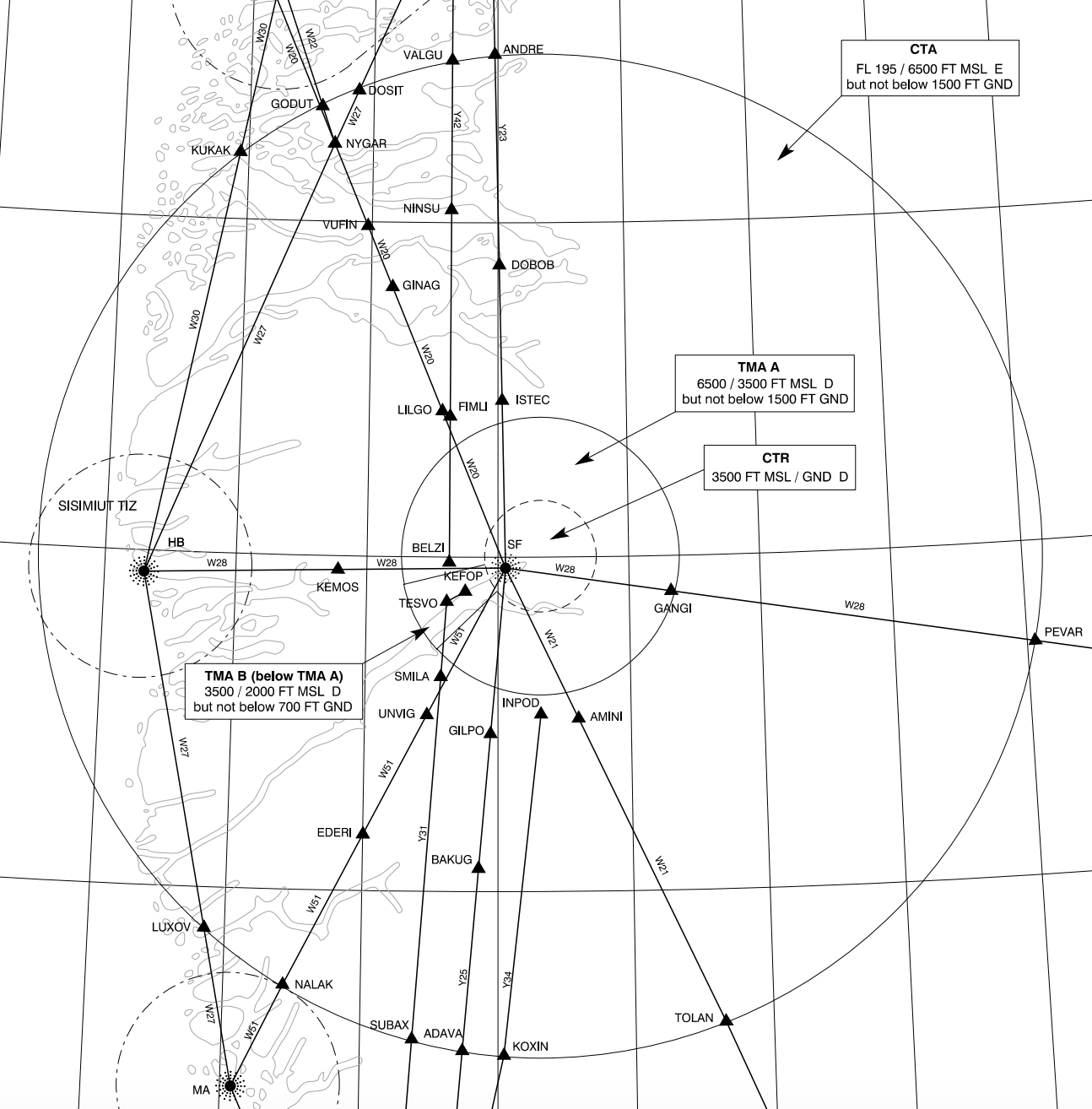
Sondrestrom TMA & CTA
The Sondrestrom TMA and CTA together make up the airspace controlled by Sondrestrom Approach.
The CTA and TMA are arranged as three sections of cylindrical airspace.
- The CTA (6500ft – FL195) is the largest cylinder of airspace.
- TMA A (3500 – 6500ft), the main portion of the TMA, forms a smaller cylinder beneath the CTA.
- TMA B (2000 – 3500ft) is a small cylindrical segment, extending the TMA downwards to encompass the RWY 09 approach path. It directly underlies TMA A.
Arrivals
Runway 09
There are no STARs into BGSF. Aircraft generally join the instrument approach procedures directly from their flight plan route.
The RNP approach for RWY 09 is the preferred approach type. Aircraft should be cleared to either of the IAFs (DODIP or BELZI) and descended to the initial approach altitudes as published:
- DODIP: 5200ft
- BELZI: 4900ft
Missed Approach
TWR shall instruct aircraft to follow the standard missed approach. The standard missed approach varies between approaches:
- RNP: Climb runway track, passing 2500ft left turn direct SFT09, then direct KEFOP, climbing to 4000ft.
- LOC Z/Y: Climb on LOC course until the marker, then turn right track 103, passing 4000ft direct SF NDB, climbing to 4400ft.
- NDB Z/Y: At D2.5 ISF climb to 3000ft on track 097, then turn right direct SF NDB, climbing to 4400ft.
- RNP A/B (RWY 27): Climb on course 274, passing 3000ft direct KEFOP, climbing to 4000ft.
Strict adherence to the standard missed approaches is critical due to high terrain surrounding the airport.
TWR shall instruct aircraft unable the standard missed approach to perform a visual climb to 5000ft towards KEFOP (if on the RNP approaches) or SF NDB (if on any other approach.) Alternatively, TWR may coordinate radar vectors with APP.
TWR shall coordinate all missed approaches with APP prior to transferring back to APP.
Non-Standard Approaches (RWY 09)
If aircraft are unable to accept the RNP approach, then alternative approaches should be offered in order of precision.
LOC Z/Y
There are two published localizer approaches – LOC Z (for category A and B aircraft) and LOC Y (for category C and D aircraft.) They are both teardrop procedures, starting from SF NDB and making a left turn inbound for the localizer.
As both procedures descend into the BGSF CTR, APP should coordinate with TWR to make them aware if the approaches are used.
NDB Z/Y
There are, similarly two NDB approaches – NDB Z (for category A and B) and NDB Y (for category C and D.) They are also teardrop procedures, except instead of using the localizer, aircraft fly a final approach course towards SF NDB and the runway.
As both procedures descend into the BGSF CTR, APP should coordinate with TWR to make them aware if the approaches are used.
Runway 27
RWY 27 isWhile not usedofficially published for arrivals except by pilot request. If pilots wish to use RWY 27, though, there are two RNP approaches available which lead aircraft to RWY 27. (RNP A for categories A and B, and RNP B for categories C and D) available which line up with RWY 27.D.)
Aircraft should be cleared to one of the three IAFs (RUMAQ, FICWE, or KEFOP) and descended to the initial approach altitudes as published:
- RUMAQ: 4000ft
- FICWE: 5000ft
- RIVOP: 4700ft
Alternatively, aircraft may perform a visual circle-to-land.approach.
Circle-to-land is not permitted north of the aerodrome.
Departures
BGSF has no SIDs. As detailed in the Delivery page, aircraft follow a standard departure procedure of climbing on runway track, then passing 5300ft, proceeding direct to join their flight planned route.