EFHK - Helsinki (HEL)
Helsinki Airport is the main international airport of the city of Helsinki, and the entire country. The airport is located north of Helsinki in the neighboring city of Vantaa. The airport is operated by state-owned Finavia.
The airport is by far the busiest in Finland and the fourth busiest in the Nordic countries in terms of passenger numbers. About 90% of Finland's international air traffic passes through Helsinki Airport. On average, the airport handles around 350 departures a day.
The airport is the main hub for Finnair, the flag carrier of Finland, and its subsidiary Nordic Regional Airlines.
| IATA | ICAO | Charts |
|---|---|---|
| HEL | EFHK | Finland AIP - EFHK |
Pilot briefing
The most important information is marked with this styling.
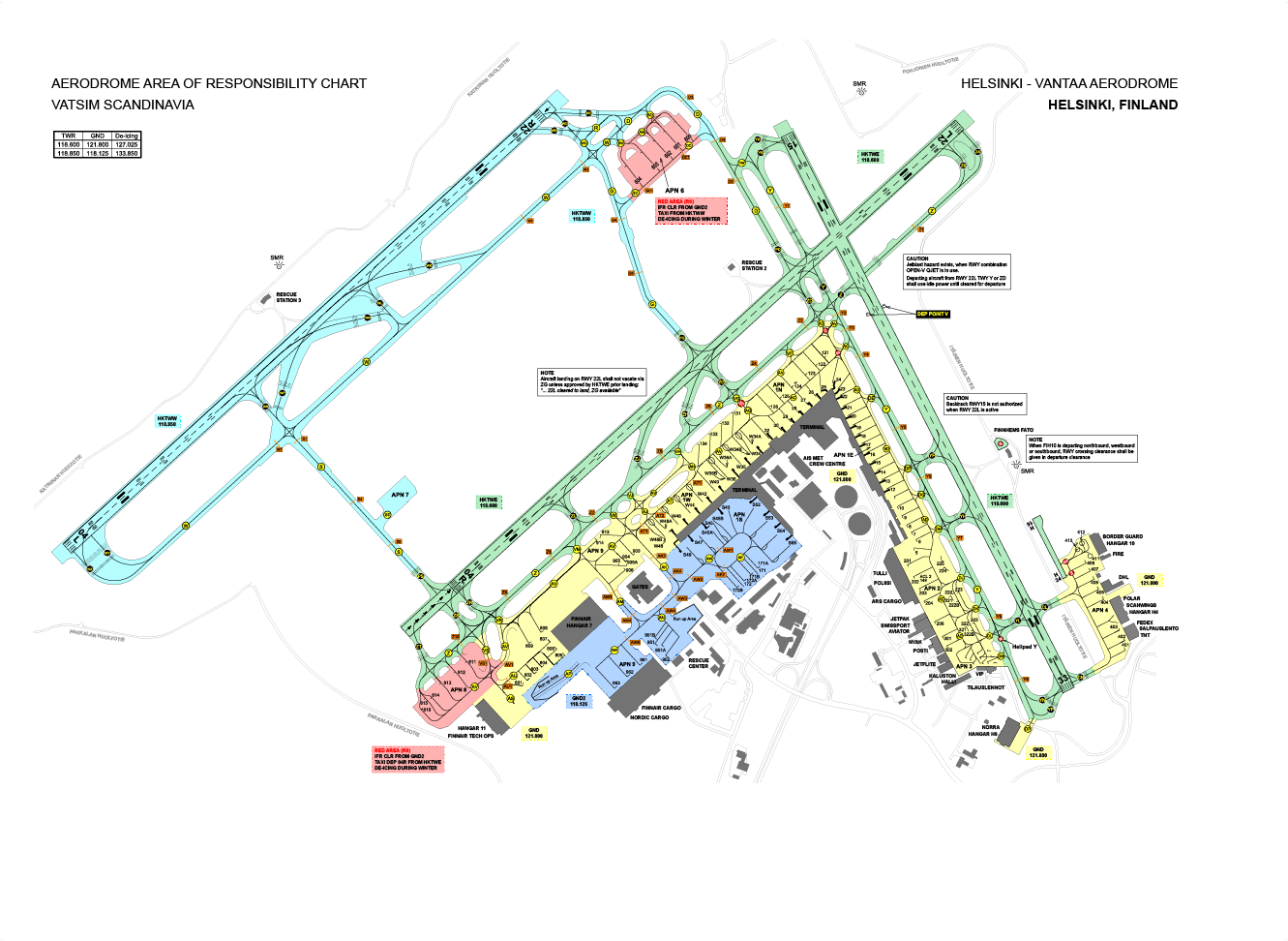
Air Traffic Control positions
Due to the size of Helsinki airport and the increased amount of operations, there is a possibility to provide service from two tower positions, two radar positions and two arrival positions:
| Login code | Call sign | Frequency | Responsibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| EFHK_DEL | HELSINKI GROUND | 118.125 | - All en-route clearances (DCL/PDC: EFHK) - Ground movement on aprons 1S and 9 |
| EFHK_GND | HELSINKI GROUND | 121.800 | - Ground movement |
| EFHK_E_TWR | HELSINKI TOWER | 118.600 | - Primary Tower position - Runways 04R/22L and 15/33 - FATO H16/H34 |
| EFHK_W_TWR | HELSINKI TOWER | 118.850 | - Opened according to traffic demand - Runways 04L/22R |
| EFHK_E_APP | HELSINKI RADAR | 119.100 | - Primary Radar position - East sector |
| EFHK_E_APP | HELSINKI RADAR | 129.850 | - Opened according to traffic demand - West sector |
| EFHK_R_APP | HELSINKI ARRIVAL | 119.900 | - Primary arrival position - Sequencing arriving traffic below 5000 FT |
| EFHK_A_APP | HELSINKI ARRIVAL | 124.325 | - Opened only during parallel IFR approaches - Sequencing arriving traffic below 5000 FT |
Listen carefully to the frequency given when being transferred to another controller. Do not try and guess the next frequency, as TWR and APP units may be divided to smaller sectors with similar frequencies.
Ground movement responsibilities:
| EFHK_DEL 118.125 |
EFHK_GND 121.800 |
EFHK_E_TWR 118.600 |
EFHK_W_TWR 118.850 |
DE-ICING |
Currently available stands
Stand allocation:
Fun fact! Most of the stand numbers starts with the apron number.
| Type | Stand location |
|---|---|
| Schengen | stands 12-32 and remote stands |
| Non-Schengen | stands W34-W48, S49-S55 and remote stands |
| Cargo | aprons 2, 4 and 9 |
| General Aviation / VIP | apron 3 |
| Stands reserved for de-icing during winter season | aprons 6 and 8 |
Taxi procedures
Taxiing on the apron is always subject to instructions. If you are unsure where to go, please ask for detailed taxi instructions.
Note that the main taxiways have only one letter, e.g. "Y" or "Z", but most taxiways are named with two letters, e.g. "AD" or "AC". Listen carefully to the taxi instructions given by ATC.
The use of Apron Spots is rare, but may be used as coordination points for both inbound and outbound traffic to and from aprons. Apron spots are marked with a painted circle on the centerline of the taxiway. When cleared to an apron spot, the pilot shall stop the aircraft nose over the marking.
Do not cross a runway without a specific clearance from ATC.
Keep the transponder active (squawk mode C) at all times when moving on the runways, taxiways and aprons.
Taxi procedures for departing aircraft
When runway 22R is in use for departure, expect to hold short of runway 22L before you are given clearance to taxi to holding point runway 22R.
By
will Grounddefault, movementATC responsibilities:
| Runway | Holding point | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| 04L | ... | |
| 04R | Aircraft from Apron 8: ZS, ZT | |
| 15 | Turboprop aircraft DEP from Z | |
| 33 | Aircraft from Apron 4: CN | |
| 22L | Turboprop/QJet aircraft DEP from Y/ZD | |
| 22R | WG, WD | WL may be used for traffic from taxiway S |
Taxi procedures for arriving aircraft
ATC will often use minimum spacing on final approach. It is important to vacate the runway quickly in order to achieve maximum runway capacity and minimize the occurance of go-arounds.
When landing on runway 22L, vacate via ZH or later. Do no vacate via Y, ZD or ZG without prior approval from Helsinki Tower.
When landing on runway 04R/22L or 15/33, contact Helsinki Ground 121.8 after vacating the runway. No handoff will be given.
Keep the transponder active (squawk mode C) until parked on the assigned stand, whichafter pilot shall select transponder code 2000 and turn off the transponder.
Preferential runway system
When ATC is online, the runway is selected according to the following wind limits when possible. Note that runways may differ from real life due different traffic amount and type. Controllers on VATSIM will select the most suitable runway according to the traffic needs on VATSIM.
| Preference order: | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arrival runway: | 15 | 22L | 04L | 04R | 22R | 33 |
| Departure runway: | 22R | 22L | 04R | 33 | 04L | 15 |
As a general rule, the first available preferential runway will be used until the crosswind component on a dry runway exceeds 20 KT and/or the tailwind component exceeds 5 KT. If the runway is contaminated, the respective restrictions are 15 KT and 5 KT.
DEPARTING AIRCRAFT
Pilots are requested NOT to include SID in their flight plan as this will be assigned by ATC.
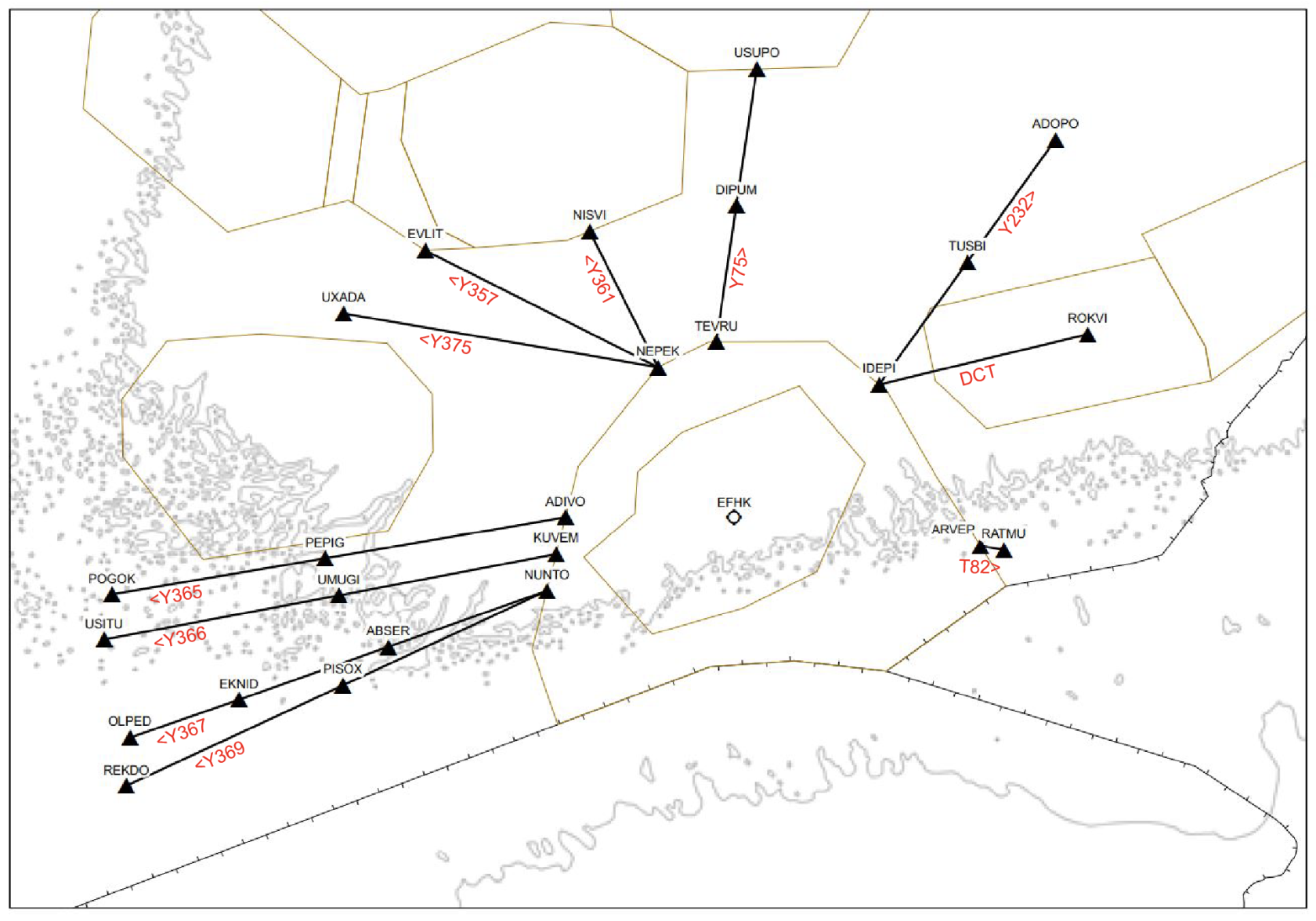
Mandatory departure routes
IFR-flights departing from Helsinki above FL 95 shall use these mandatory routes after the SID:
After the last point of the mandatory departure route, pilots have mostly free hands to plan their flights with DCT routes.
RENKU is only available and mandatory for departures to EETN or EEEI. Maximum cruise level is FL 100.
En-route clearance
En-route clearance can be requested with DCL (datalink) or with VOICE over the ground or tower frequency depending on which ATC position is online.
If using DCL, pilots shall send the pre-dep request to identifier EFHK or EFIN, depending on which station is online. Frequency 118.125 shall be monitored when requesting clearance via DCL.
On initial contact, state aircraft type, received ATIS and QNH.
If you prefer to use a different runway due performance, you may ask it prior to receiving the en-route clearance. Runways 22L and 15 are often approved for turboprop or quiet aircraft.
If unable to follow RNAV SID, inform ATC when requesting clearance.
Your en-route clearance will include the destination, departure runway, SID or heading and the initial climb which is usually 4000 feet. You will also receive an SSR-code which shall be selected and activated prior to taxi.
Runway holding points
By default, ATC will use these holding points:
Take-off and climb
When cleared for take-off, pilots are expected to start rolling within 10 seconds of take-off clearance. Pilots unable to comply with this requirement shall notify ATC before entering the runway.
RADIO TRANSFER PROCEDURES:
After take-off aircraft shall remain on tower frequency until passing 1500 FT, then contact Helsinki Radar 119.100 or 129.850, depending on your SID route.
You will find the correct radar frequency on your SID-chart. If the primary frequency is not online, contact Radar on the other frequency or Helsinki Control on 121.300.
Pilots shall automatically change to radar frequency after departure!
INITIAL CONTACT WITH RADAR AFTER DEPARTURE:
When contacting Helsinki Radar, state your altitude and assigned SID. If you are assigned a heading, report the heading to Radar on initial contact.
If no further climb is given, pilot shall maintain 4000 FT.
ARRIVING AIRCRAFT
Arriving traffic is informed of the runway in use and cleared for the appropriate STAR serving the arrival runway. This information is given by Area Control (EFIN/EETT) when online.
Radio Transfer Procedures
Phraseology examples to be used during initial contact with the respective ATC-units:
INITIAL CONTACT WITH APPROACH CONTROL
| Call sign | HELSINKI RADAR, FINNAIR 6 |
|---|---|
| Aircraft type | AIRBUS 330 |
| “HEAVY” or “SUPER” if necessary | HEAVY |
| Current flight level | FLIGHT LEVEL 154 |
| Speed (only if assigned by ATC) | SPEED 240 KNOTS |
| Last received ATIS broadcast | INFORMATION SIERRA |
INITIAL CONTACT WITH ARRIVAL (CALLSIGN ONLY!)
| Call sign | HELSINKI ARRIVAL, FINNAIR 6 |
|---|
INITIAL CONTACT WITH AERODROME CONTROL
| Call sign | HELSINKI TOWER, FINNAIR 6 |
|---|---|
| Runway | RUNWAY 22 LEFT |
Clearance for Approach
There are 2 ways to be cleared for the approach:
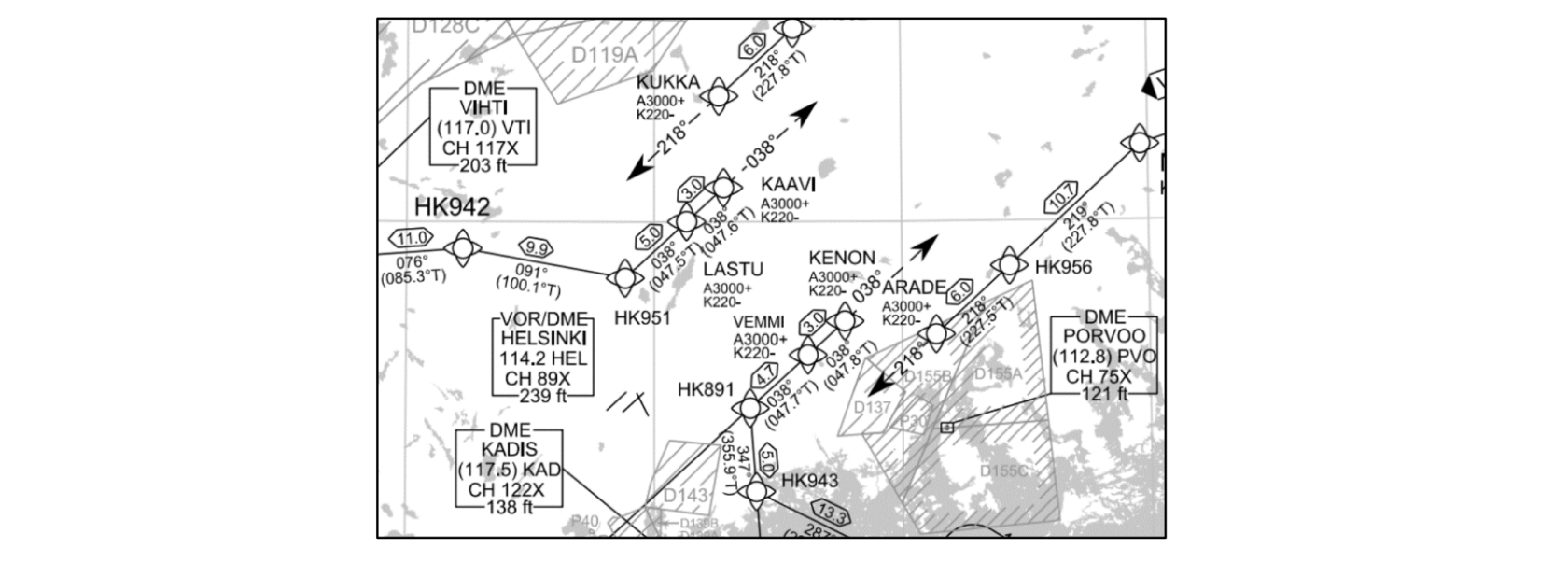
CLEARANCE FOR APPROACH VIA OWN NAVIGATION
All STARs at Helsinki are so-called Open STARs. If ATC has not given approach clearance, the pilot shall continue present heading after the last waypoint on the STAR:
When aircraft is cleared for approach via own navigation, pilot shall plan a direct (DCT) instead of a vector after the last waypoint on the STAR.
| 🎧 | SPEEDBIRD 794H, VIA KENON BIFIX CLEARED ILS APPROACH RUNWAY 22 LEFT |
VISUAL APPROACH
ILS is the primary approach type. Upon pilot request, ATC may give clearance for a visual approach.
ATC may advise to “maintain own separation from preceding”, if there are other aircraft approaching the airport. In that case, the separation responsibility will transfer from ATC to the pilot performing the visual approach.
Aircraft on visual approach shall maintain at least 2000 FT until established on final approach course. ATC may give permission “you may leave 2000 feet before final”.
SIMULTANEOUS IFR APPROACHES
During periods of heavy inbound traffic, dependent or independent simultaneous approaches may be used on runways 04L/R or 22L/R.
Pilots are informed when parallel approaches are in force via ATIS:
Simultaneous independent IFR approaches in progress.
Area control will inform the landing runway as early as possible; however, pilots should plan on landing on either runway when parallel approaches are in progress.
Mandatory arrival routes
Pilots are requested to not include STAR in their flight plan route.
Arriving IFR flights with cruising level above FL 95 shall use the following routes:
...