ESSA - Stockholm/Arlanda
Overview
Stockholm Arlanda Airport is Stockholm’s main airport and the largest and busiest airport in Sweden. It is located around 40 km north of the city of Stockholm. The airport was officially opened in 1962, although the first aircraft had landed there several years earlier. Arlanda is serviced by over 70 airlines with around 170 destinations. Around 26 million people pass through the airport annually. Arlanda is also an important cargo hub.
Arlanda originally had two runways (01/19 and 08/26). A third runway, 01R/19L, was opened in 2003 to the east of the airport.
Airport Charts
Parking stands
Available stands
Stand allocation - Who parks where
Who parks where - Arlanda airport website
The airport website shows the real gate for each DEPARTING and ARRIVING flight.
- Terminal 2 (Stand 62-68) - Schengen and non-Schengen
- Terminal 3 (Stand 52-60A) - Domestic turboprops
- Terminal 5
- Stand 31-44 - Schengen
- Stand 1-20 and F28-F44 - Schengen and non-Schengen
- Apron E (Stand 101-119) - Remote stands and long-term parking
- Apron G (Stand G141-G149) - Remote stands for smaller aircraft (turboprops/CRJ)
- Apron H - SAS Maintenance and long-term parking
- Apron J - VIP and Ambulance flights
- Apron K (Stand K1-K5) - Large GA, VIP flights and long-term parking
- Apron L - Patria Helicopters (maintenance facility, helicopters refuelling when ESSB closed)
- Apron R (Stand R3-R10) - Cargo flights
- Apron S - Small GA, cargo and small turboprops
Operations with large aircraft
Aircraft with wingspan more than 65 m (e.g. A388, A124, A225, B748, A345/6, B779 and C5/5M).
A388, A124, B748, A345/6, C5/5M
- Landing: RWY 01L/19R or 26 shall be used.
- RWY exit Y1, Y9, Y10 or X2 shall be used.
- Take-off: RWY 01L/19R shall be used.
- RWY entry Y1, Y9 and Y10 shall be used.
- Taxiing: TWY Y, PA, X (Y-ZQ) and U (Y-EA) shall be used.
- Parking at stand F36R, 104, R9 or R10.
A225
- Landing/take-off: RWY 01L/19R shall be used.
- RWY exit/entry Y1 or Y10 shall be used.
- Taxiing: TWY Y, U and UE shall be used.
- Parking at stand R9 or R10.
IFR Clearance
At first contact with Clearance Delivery state type of aircraft, stand number and latest received ATIS transmission including identification letter and QNH.
- If a different runway than the runway-in-use is required for performance reasons, this request shall be made in connection with the request for IFR clearance.
- If unable to follow FMS/RNAV SID, inform ATC when requesting clearance. Expect to be assigned a SID and to follow the “unable RNAV SID instruction” given in the SID chart.
SID Assignment
Unless otherwise instructed, aircraft cleared via SID shall climb to 5000 ft.
Some SID designators are based on a point just before the first flight planned point. For example, if flight planned via ARS and departing RWY 19L the SID could be ARS 5E or ROKNI 5Q. Be careful to fly the correct departure.
Low speed departures
Between 0600 and 2200 local time, low speed aircraft (including most propeller driven aircraft, but exccluding some faster types such as Saab 2000, and Dash 8-Q400 among others) are normally cleared via radar vectoring with initial climb clearance to 3000 ft instead of SID, or via HAPZI SID when RWY 19R is in use.
Startup approval
When simulating A-CDM departure procedures, Clearance Delivery will give a Target Startup Approval Time or TSAT. Report ready to Clearance Delivery within TSAT +/- 5 minutes. Clearance Delivery will give instruction to contact the appropriate Ground frequency. Ground will give approval for startup, and for push-back where required.
Push-back
Push-back is generally required for all jet aircraft, unless parked at Terminal 3, Apron R stand R9C, Apron G stand G149 or Apron S stand S71-S79.
Push-back procedure charts available from the Arlanda airport website
If using GSX with an appropriate config file for ESSA, GSX will push you to the standard positions according to the document above.
Use of transponder
The assigned transponder code shall be selected and the transponder activated at the request for push-back. After landing, the transponder shall remain activated until reaching the parking stand and be switched to standby immediately after parking.
Deicing
Deicing is normally performed before push-back, except for traffic from terminal 2 where it is done after push-back before taxi.
Taxi
Unless otherwise instructed by ATC, the standard taxi routes shall be followed.
After landing: If no taxi instructions have been received, make sure you have fully vacated the runway, and hold before the first parallel taxiway and wait for taxi instructions.
Overview of standard taxi procedures
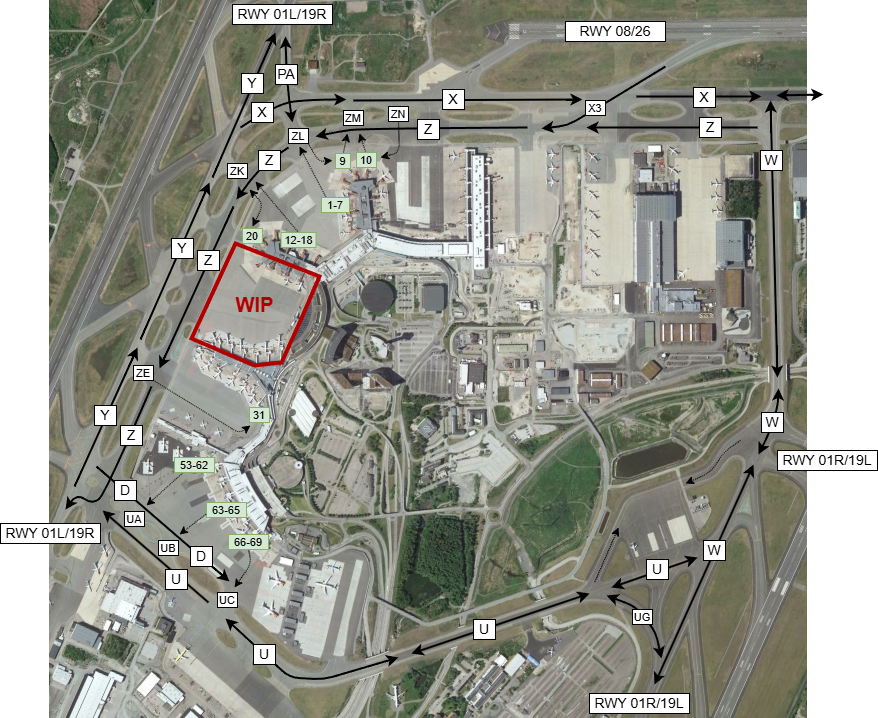
Refer to airport charts (Aerodrome ground movement chart/DEPARTURE or ARRIVAL) for actual procedures.
Taxi clearances will normally not include the complete taxi route, as pilots are expected to follow the standard taxi routes. When RWY 01R/19L is in use, pilots will be instructed to use TWY W or U.
Take-off and climb
Unless otherwise instructed, aircraft cleared via SID shall climb to 5000 ft.
Contact Stockholm Control when instructed by TWR. On initial contact with Stockholm Control report altitude to verify transponder Mode C readout.
STAR
Observe the maximum flight levels at the TMA entry points.
Plan your descent into Stockholm TMA according to the level restrictions depicted on the STAR charts.
Speed restrictions
Maximum speed in Stockholm TMA below FL100 is 250 knots, unless otherwise instructed by ATC.
Aircraft shall maintain minimum 160 knots until OM or 4 NM final or advise ATC if unable.
RNP approaches
Curved (RNP AR) and straight RNP approaches are available on request.
Independent parallel approaches
Independent parallel approaches at ESSA are carried out using the Established on RNP concept. This means ILS approaches are conducted on the "main" landing runway (01R/19L) while RNP AR approaches are conducted independently on the parallel runway (01L/19R).
RNP AR capable aircraft will be identified to ATC by the ICAO PBN “T1” code on the flight plan. Aircraft that have filed “T1” are expected to have RNP AR capability. If this is not the case, flight crew shall inform ATC as soon as possible and can expect an ILS approach.
ATIS will indicate when simultaneous independent parallel runway operations are in effect.
Operational requirements
- The RNP AR approach shall be flown from the IAF published on each RNP AR procedure.
- The RNP AR approach shall be flown using autopilot.
- When cleared for an RNP AR approach, the aircraft shall report “ESTABLISHED” on the approach procedure before reaching the intermediate approach fix (IF). Once established, the aircraft will be considered separated from aircraft conducting ILS approach on the adjacent parallel runway.
- If, after an aircraft has been cleared on an RNP AR procedure, the aircraft becomes unable to continue executing the procedure or adhere to the containment of the RNP AR procedure, ATC shall be notified immediately , and the pilot shall be instructed to execute an appropriate breakout procedure.
- When EoR operations are in use, breakout instructions and phraseology shall be briefed prior to approach clearance being received. This applies both to aircraft conducting the RNP AR approach and to aircraft conducting ILS approach to the adjacent parallel runway.
- Approach clearances, charted altitude and speed constraints shall be complied with. The lateral and vertical path shall be monitored to ensure precise navigation accuracy.
- If unable to comply with an ATC clearance or conduct the RNP AR approach, advise ATC as soon as possible. Do not attempt to manually correct or self-navigate an RNP AR approach procedure deviation.
- If an arriving aircraft is established on the RNP AR approach procedure and the aircraft is no longer able to execute it, immediately advise ATC using the following phraseology, then comply with subsequent ATC instructions: UNABLE RNP, REQUEST (proposed course of action)
Breakout procedures
Between the extended centerlines of the parallel approaches, a no transgression zone (NTZ) is established. In case an aircraft penetrates the NTZ, the conflicting aircraft on the adjacent parallel approach will be instructed to perform a breakout procedure.
A breakout procedure can be issued on the approach or tower frequency. No dual-frequency monitoring is required.
BREAKOUT [Callsign]. TURN LEFT/RIGHT (immediately) HEADING XXX AND CLIMB TO XX FT. Example: “BREAKOUT NOZ816, TURN LEFT HEADING 330, CLIMB TO 2500FT”
EoR break-out procedures should be conducted with the autopilot on.
NOTE: When issued breakout instructions, reaction time is critical. If expeditious compliance is required, an ATC breakout instruction will include the word “IMMEDIATELY.”
Visual approach
Visual approach is only permitted if approach aids are unserviceable or to avoid significant weather conditions.
Missed approach
Missed approach procedures have a level-off altitude of 1500 ft.
Do not climb above 1500 ft unless cleared by ATC.
Use of runways
The runway combinations used at Arlanda are based primarily on flight safety, traffic intensity, noise abatement procedures, and wind and visibility. Request for a different runway can be made for performance reasons only.
During peak hours expect one of the following runway combinations:
- Landing RWY 01R / Departure RWY 01L
- Landing RWY 19L / Departure RWY 19R
Off-peak the following runway combinations are the most common:
- Landing RWY 26 / Departure RWY 19R
- Landing RWY 19R / Departure RWY 08 (Right turn out)
- Landing RWY 01L / Departure RWY 08 (Left turn out)
- Landing RWY 26 / Departure RWY 01L (VMC)
- Landing RWY 01R / Departure RWY 01L (IMC)
Note:
- Landing RWY 08 or Departure RWY 26 is only used if no other alternatives are available.
- At night (between 22 and 07 local time) Departure RWY 19R is only available for performance reasons.
Runway selection is at the discretion of ATC. The runway combination used on VATSIM may differ from what is used in reality.
